Application Architecture
A modern application emphasizing security
The dbFLEX application architecture is as follows:
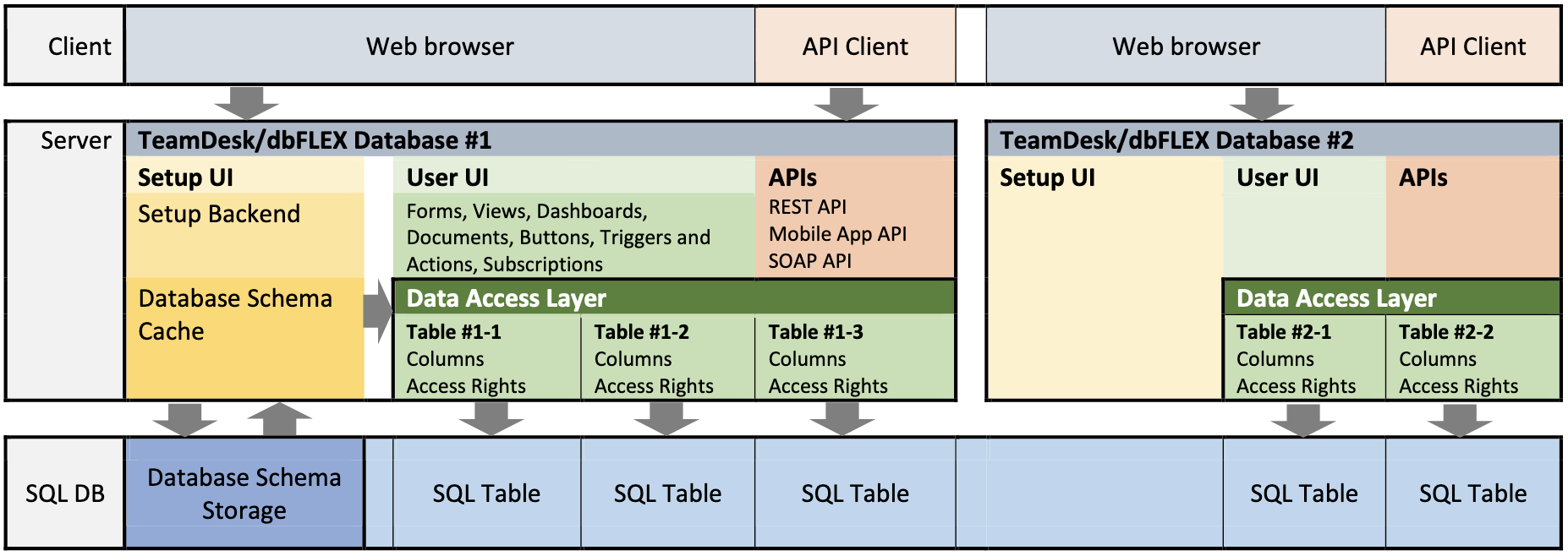
- dbFLEX provides a logical view of the SQL database.
- While multiple customers may share a global SQL database (as is likely the case for most cloud SaaS and PaaS providers), the data is strictly isolated using a component called the "Data Access Layer" or "DAL" for short. The DAL is the only component that has direct access to the database.
- For example, when a user accesses a "View" (e.g. a data sheet, rolled up summary, or a chart):
- The View is created under a Table, and is comprised of columns and filters.
- The app page that will display the View passes the access request to the DAL.
- The DAL examines the data definition (metadata), checking whether the table belongs to the database, and whether the current accessing user has enough access rights to view records from the table, and further, to individual columns.
- If any column is not accessible, the request is either rejected completely (i.e. in the case that the view's filter column happens to be inaccessible to the user) or the column is hidden from view (if it's in the list of columns to display).
- Once all verifications pass, the DAL builds and executes an SQL query to retrieve the data, and the results are passed back to the requestor.